While a number of new systemic antifungals have been licensed in recent years (most recently isavuconazole), there is still an urgent need for new drugs, particularly from novel chemical classes – as reviewed by Perfect (2017) in Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. Shortcomings of current drugs include:
- Toxicity and unpleasant side effects
- Suboptimal pharmacokinetic properties, such as short half-life or poor penetration into certain tissues or sanctuary sites
- Antifungal resistance (intrinsic or acquired)
It should be noted that many FDA-approved antifungals (especially newer formulations) are unavailable to patients in many healthcare systems due to cost and in some cases lack of local registration.
New antifungals in human trials
For a full list of clinical trials please visit Clinicaltrials.gov (NIH worldwide) or NIHR Be Part of Research (NHS, UK).
Recent progress on new antifungals currently in Phase 2 or 3 trials was reviewed in Science by Kupferschmidt (2019).
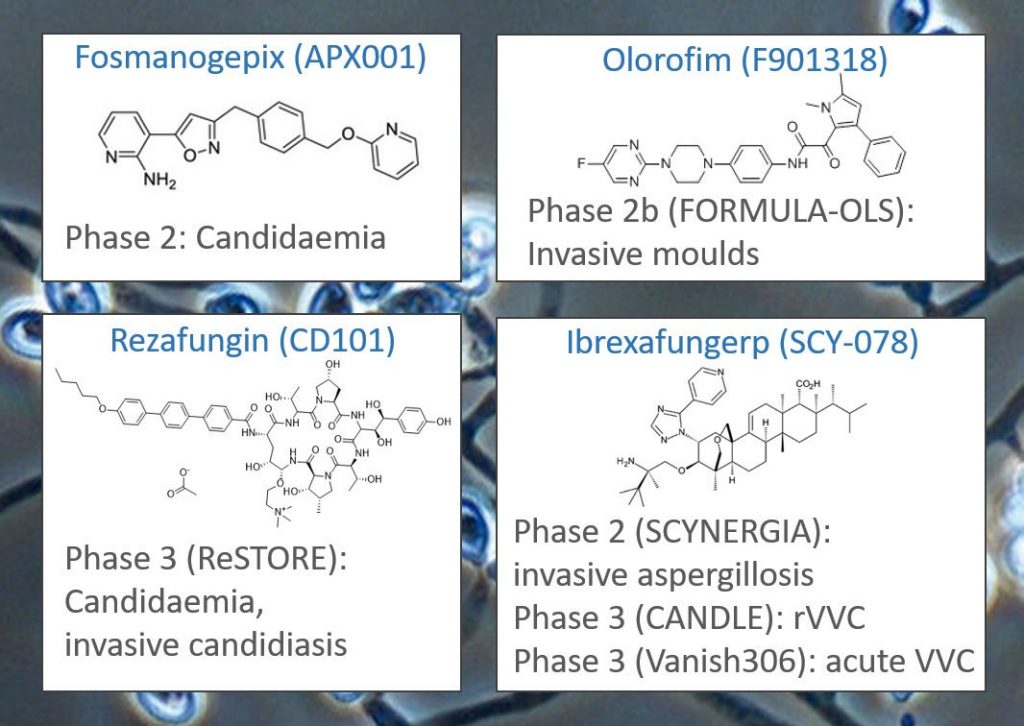
@AmplyxPharma are sponsoring a Phase 2 trial (NCT03604705) testing fosmanogepix (APX001, a fast-tracked first-in-class Gwt1 inhibitor) against candidaemia.
F2G are sponsoring a Phase 2b trial (FORMULA-OLS, NCT03583164) testing olorofim (F901318, an orotomide) against invasive fungal infections (Aspergillus, Fusarium, Lomentospora, Scedosporium, invasive infections) in ~100 patients lacking other treatment options.
@CidaraThera are sponsoring a Phase 3 RCT (ReSTORE, NCT03667690) testing IV rezafungin (CD101, an echinocandin) against candidaemia and invasive candida in ~218 patients (placebo = IV caspofungin).
Several trials by @Scynexis are underway for ibrexafungerp (SCY-078, first-in-class triterpene), including as combination therapy with voriconazole for treating invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (Phase 2, SCYNERGIA, NCT03672292). It is also in Phase 3 trials for recurrent vulvovaginal thrush (CANDLE, NCT04029116) and acute vulvovaginal thrush (Vanish306, NCT03987620).

New antifungals in discovery or preclinical phases
For more information and recent publications please see the New Antifungals section of the Aspergillus & Aspergillosis website.

Other interventions
Many clinical trials are underway for purposes other than registering new antifungals, for example:
- Diagnostics and biomarker-directed treatment selection
- Devices (e.g. antifungal central line locks)
- Delivery systems (e.g. inhaled amphotericin, clotrimazole socks)
- Regimens and combined therapies
- Antifungal stewardship
