Hundreds of thousands of cases of Pneumocystis lung infections are seen each year, primarily in immunosuppressed patients.
Clinical lectures
Click here to download the slide decks for the lectures
Assessing hypoxaemia in Pneumocystis patients
Pneumocystis microscopy
Pneumocystis management in children
Pneumocystis presentation in children
Prophylaxis for Pneumocystis
Pneumocystis coinfections
Beta-D-glucan testing (Dynamiker kit)
Beta-D-glucan testing (Fungitell kit)
Beta-D-glucan (Goldstream kit, Era Biology)
Beta-D-glucan (webinar + Q&A) fungal diagnostics – invasive Aspergillus Pneumocystis Candida

Factsheet
| NAMES Pneumocystis pneumonia, PCP, PJP, Pneumocystis pneumonitis |
| DISEASE – In HIV/AIDS patients, PCP is a subacute disease with fever, cough, weight loss, diarrhoea and increasing breathlessness. Prodromal features are often present for two to three weeks before the breathlessness becomes clinically problematic. – In other immunodeficient patients, PCP is a more rapidly progressive disease with more prominent radiological findings and wheeze. |
| FUNGI Pneumocystis jirovecii (formerly carinii) |
| GLOBAL BURDEN Worldwide distribution. ~2.8 million with advanced HIV/AIDS infection are at risk. Conservative estimates suggest ~400,000 cases annually, but this is likely to be an underestimate of the true burden. PCP rates rise with GDP and decreasing numbers of TB cases, but the reasons for this are unclear. |
| RISK FACTORS HIV/AIDS patients with CD4 cells <250 x 106/L (and especially <200 x 106/L). Transplant recipients, corticosteroid-treated patients (e.g. those with brain tumours on dexamethasone), malnourished children. Patients with hypogammaglobulinaemia, or acute/chronic leukaemia, or lymphoma. |
| DIAGNOSIS – SPECIMEN: usually induced sputum and BAL fluids. Spontaneously-produced sputum and oral mouth-wash samples can also be used. – DETECTION: best with real-time PCR or immunofluorescence. Beta-D-glucan is usually raised in blood and can assist with diagnosis. Culture is not possible because the microorganism does not grow in any known culture media. There is a new PCR assay being tested for efficacy against PCP. Lung or other tissue biopsy and subsequent histology are sometimes necessary for diagnosis. |
| TREATMENT – First-line: cotrimoxazole/trimethoprim with corticosteroids for moderate or severe disease. – Second-line: pentamidine or combination of clindamycin/primaquine. Mild cases can be treated with trimethoprim and dapsone or atavaquone. |
| OUTLOOK If diagnosed promptly, the survival is 80-90% in HIV/AIDS in the western world. In non-AIDS patients, the survival is only 50%. Prevention of subsequent episodes is critical with prophylaxis, while immunocompromised. Patients with PCP should be isolated, as it is transmissible to other immunocompromised patients. |

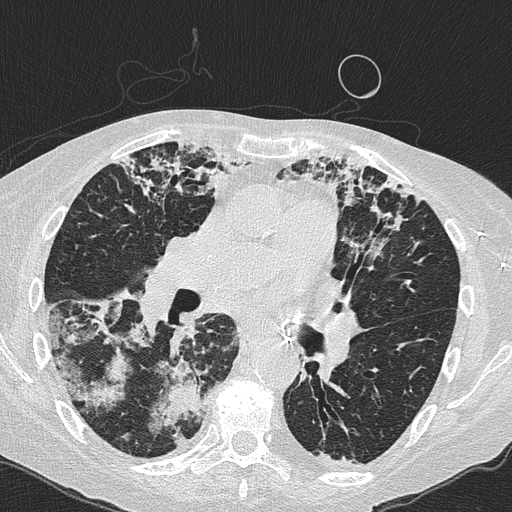
Patchy areas of consolidation with surrounding ground glass caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii in a lung transplant recipient 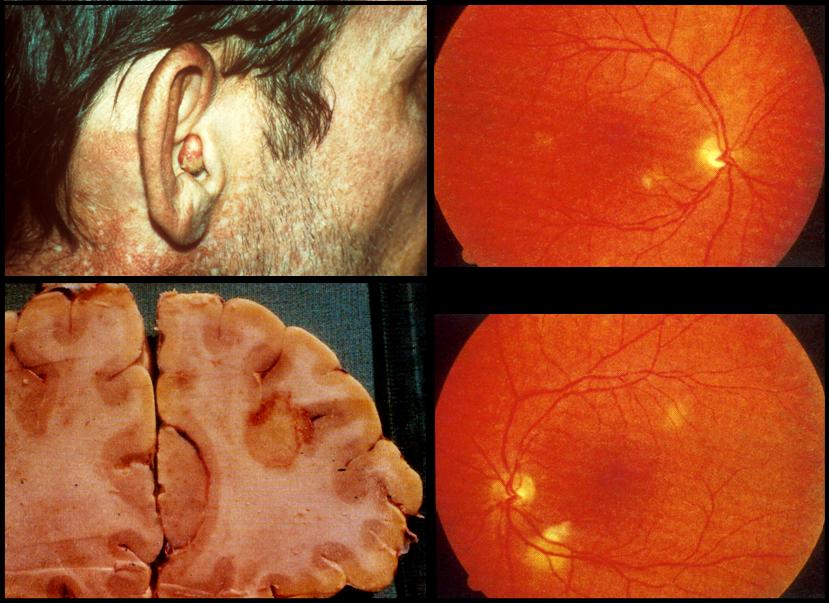
Occasionally P. jirovecii disseminated to other locations. Here are 3 examples; skin in the ear, with a nodule visible, the retina of the eye (the white blotches not where the vessels join the optic nerve) and the brain showing rounded abscesses 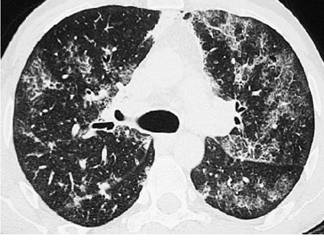
CT scan showing marked bilateral scattered opacities, some with ground glass adjacent, typical of Pneumocystis pneumonia (Courtesy of Sanjay Sharma, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi) 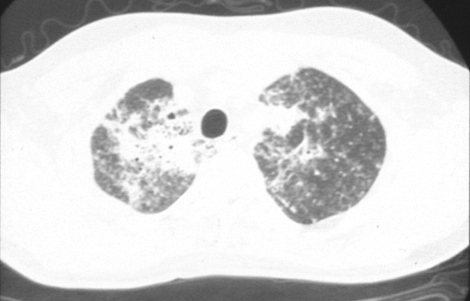
CT scan appearance of the apices in one patient with PCP showing the irregular opacities, consistent with alveolar disease 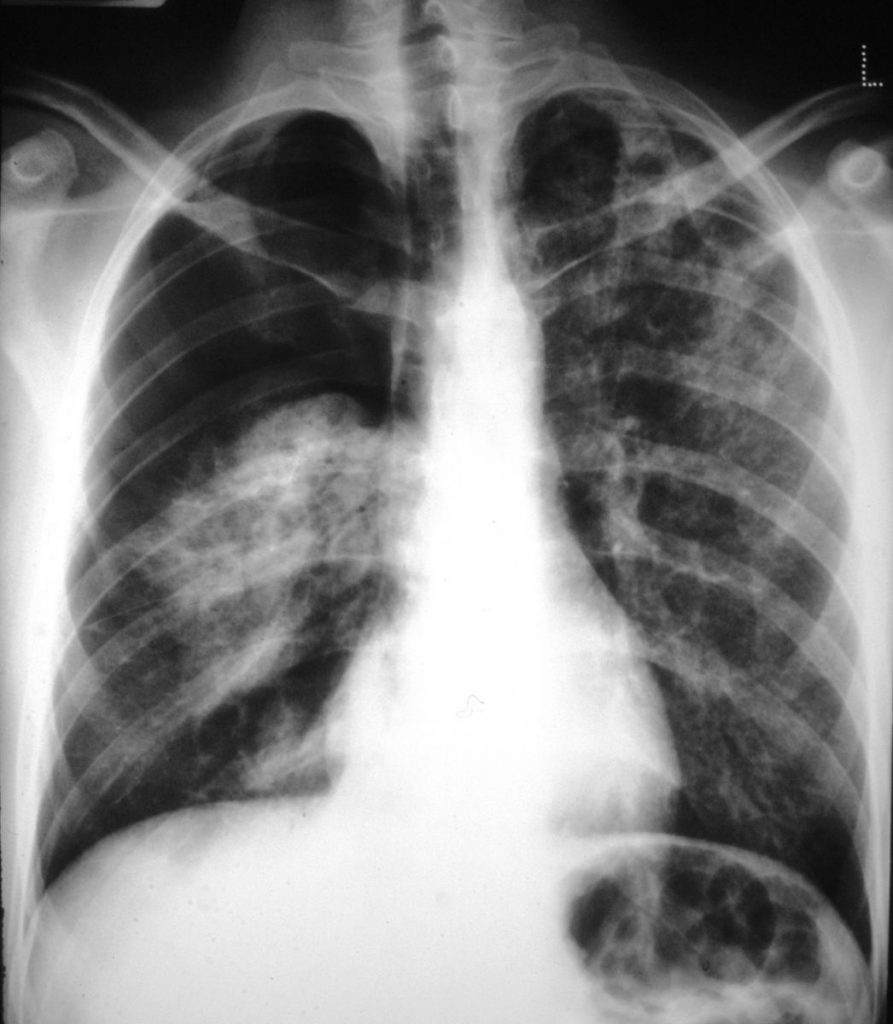
Pneumothorax in PCP (right sided), a relatively common complication 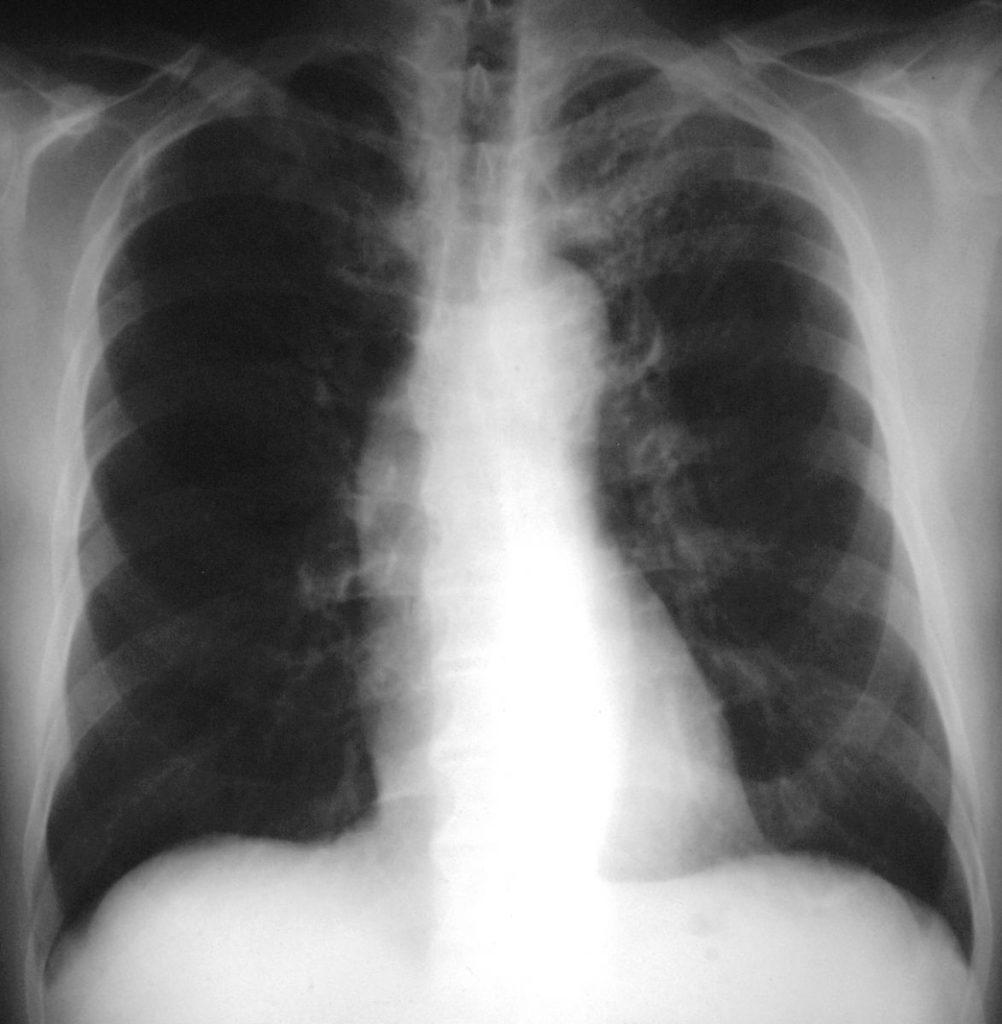
Left apical PCP, a rare occurrence, except in patients on intermittent aerosolised pentamidine for prophylaxis 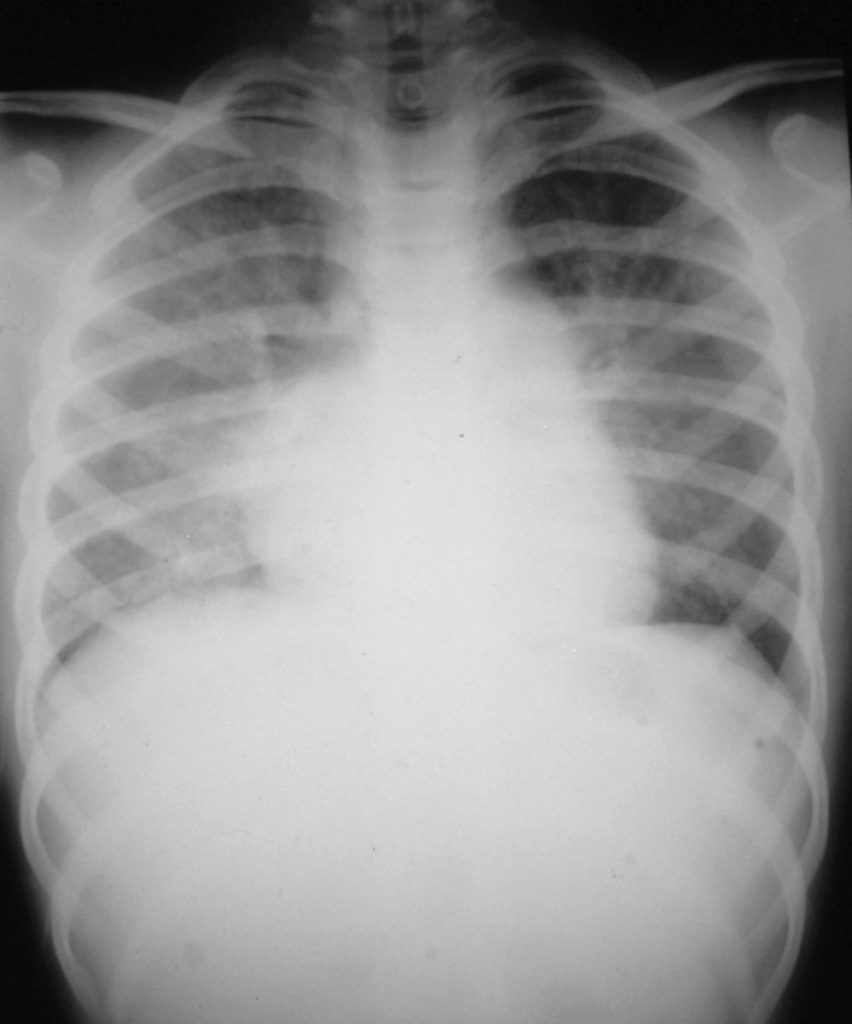
An example of PCP in a child with a lymphoma on chemotherapy, who was unable to take oral prophylaxis and developed PCP 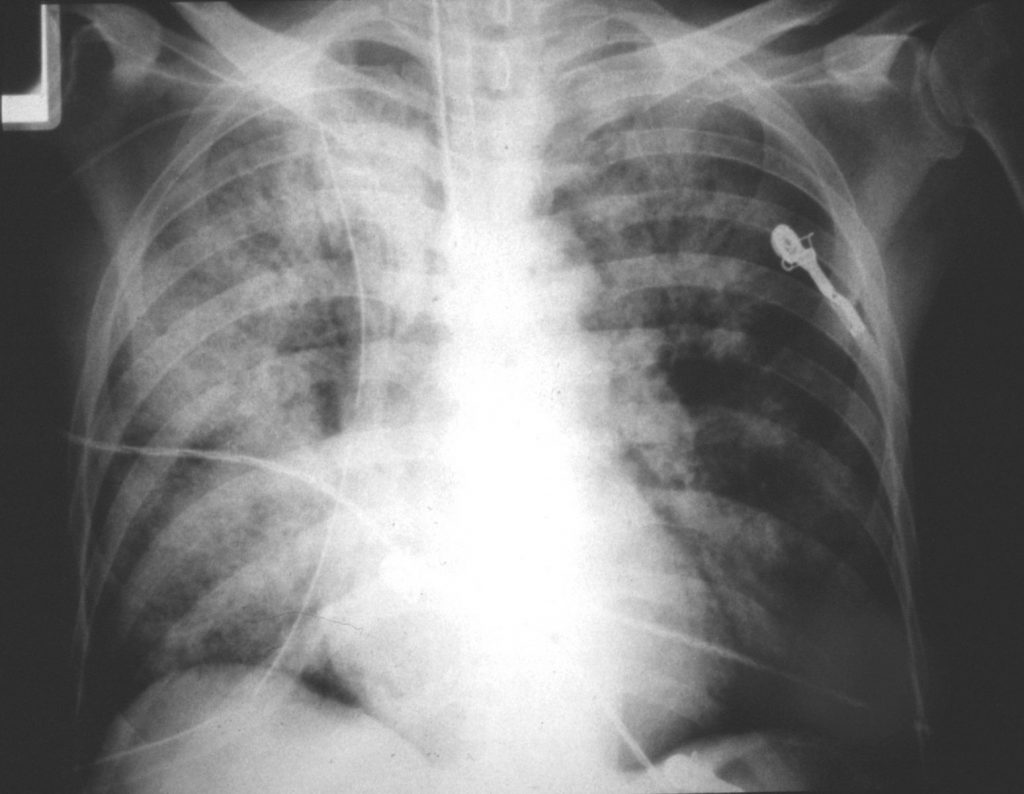
An example of severe PCP in a patient in intensive care. Most of the right lung is affected and the left upper lobe. This patient subsequently died 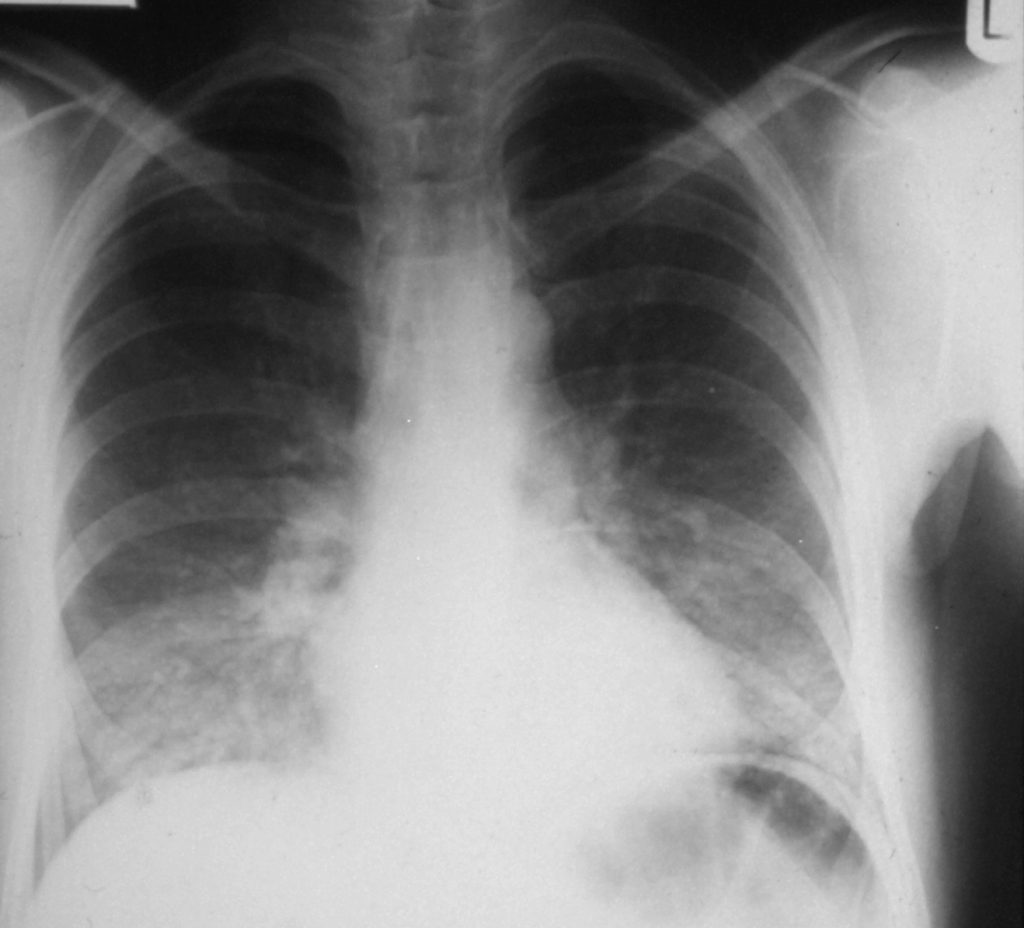
Typical example of moderately severe PCP in AIDS, with bilateral fluffy mid and lower lobe shadows
