SUMMARY: Blastomycosis is a rare fungal infection caused by inhaling spores of the fungus Blastomyces dermatitidis
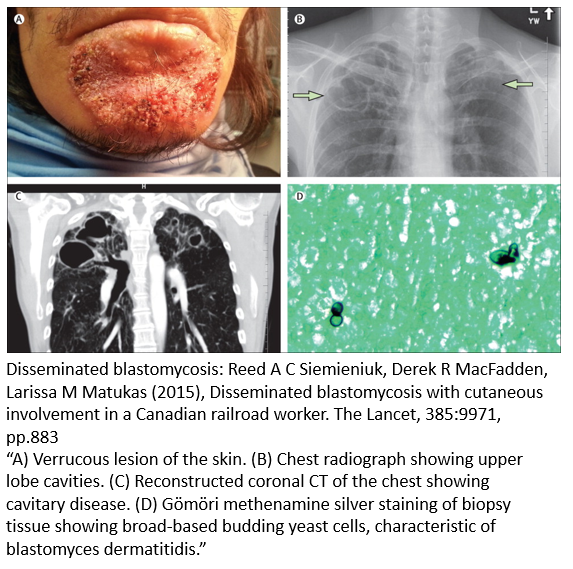
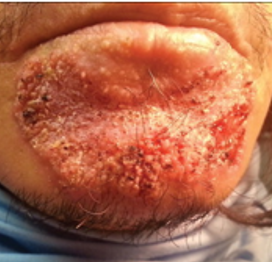
Blastomycosis is a rare fungal infection caused by inhaling spores of the fungus Blastomyces dermatitidis. The disease is endemic to areas of Canada and the USA, surrounding the Ohio and Mississippi River valley and the Great Lakes. Approximately 50% of those with blastomycosis are symptomatic, with severity ranging from flu-like symptoms to severe systemic disease.
Currently, estimated mortality rates vary between 3 and 78%; in order to assess mortality rates across published literature, and to identify risk factors for mortality, Dr Alex Carignan and colleagues analysed 23 studies published over 44 years.
Key points:
- The most valid mortality estimate was 6.6% in general cases of blastomycosis
- The mortality rate was 37% in immunocompromised patients and 75% in patients who developed an acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- Mortality rates were higher in patients over 50
The study found that the mortality estimate in general blastomycosis cases was lower than expected due to publication bias. It is likely that the review excluded several asymptomatic and autoresolutive patients, so the lethality of the disease may even be less than this. Immunocompromisation, ARDS and age of >50 were identified as risk factors for mortality. This paper reinforces recommendations that all patients with severe forms of blastomycosis should be treated with amphotericin B, though the efficacy of the different forms of the drug could not be compared due to lack of data. More studies need to be performed to identify further risk factors and compare treatment options.
Read Carignan et al (2019) Mortality associated with Blastomyces dermatitidis infection: A systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis, Medical Mycology